Scientific discoveries have significantly shaped our understanding of the world, revolutionizing various fields and leading to groundbreaking advancements. While some discoveries have garnered widespread attention and acclaim, there are several lesser-known scientific breakthroughs that have had a profound impact on our lives. In this article, we will delve into the top 5 most important scientific discoveries that are not very well known, shedding light on their significance and the impact they have had on the scientific community and society as a whole.
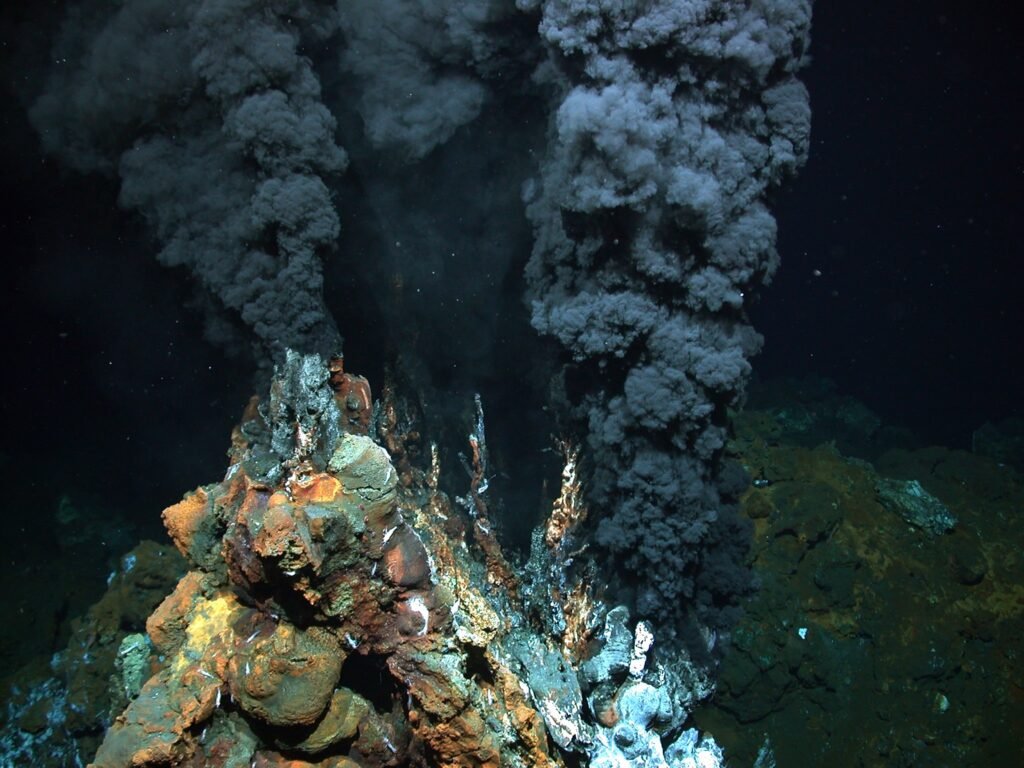
1. The Discovery of Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents
One of the most remarkable and lesser-known scientific discoveries is the finding of deep-sea hydrothermal vents. In 1977, scientists made a stunning breakthrough when they stumbled upon these otherworldly ecosystems thriving in the depths of the ocean. These vents, located along the mid-ocean ridges, are characterized by high temperatures and unique chemical compositions, creating an environment that was previously thought to be uninhabitable. The discovery of these hydrothermal vents challenged our understanding of life on Earth and provided valuable insights into the potential for life on other planets. It also revolutionized our understanding of the ocean’s geology and the cycling of elements, showcasing the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems.

2. The Identification of CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing
Another groundbreaking yet relatively lesser-known scientific discovery is the identification of the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing system. This revolutionary technology, which allows for precise and efficient editing of DNA, has immense implications for fields such as genetics, medicine, and agriculture. Discovered in the early 2010s, CRISPR-Cas9 has rapidly transformed the landscape of genetic research and holds tremendous promise for treating genetic disorders, developing genetically modified crops, and even potentially eradicating certain diseases. The discovery of CRISPR-Cas9 represents a monumental leap forward in our ability to manipulate the genetic code, opening up a world of possibilities for addressing previously untreatable conditions and advancing our understanding of the fundamental building blocks of life.

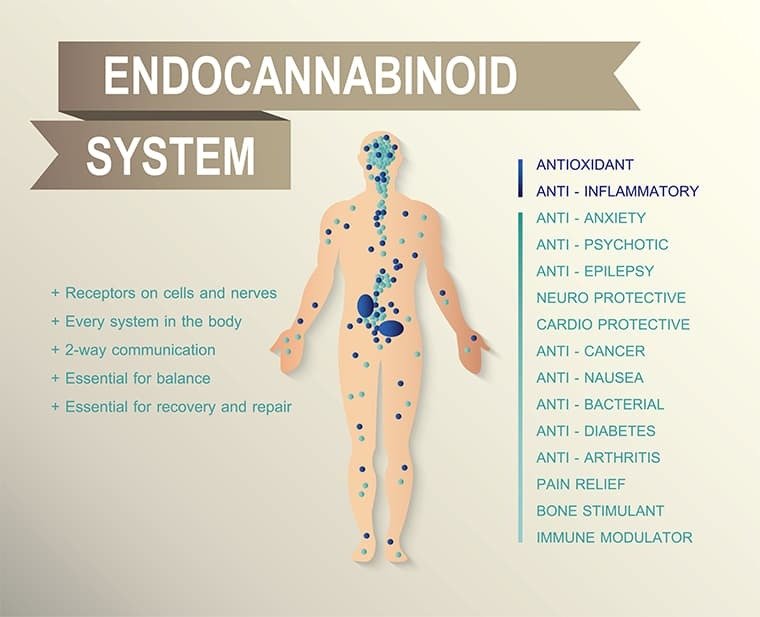
3. The Uncovering of the Endocannabinoid System
While the use of cannabis for medicinal and recreational purposes has been well-documented throughout history, it wasn’t until the late 20th century that scientists made a groundbreaking discovery related to the human body’s response to cannabis. In the 1980s and 1990s, researchers identified the endocannabinoid system, a complex network of receptors and neurotransmitters that play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes. This discovery shed light on the body’s inherent capacity to produce and respond to cannabinoids, providing a deeper understanding of how cannabis exerts its effects and paving the way for the development of novel therapeutic approaches. The endocannabinoid system has since become a focal point of research in fields such as neuroscience, pharmacology, and medicine, offering potential avenues for the treatment of conditions ranging from chronic pain and inflammation to neurological disorders.
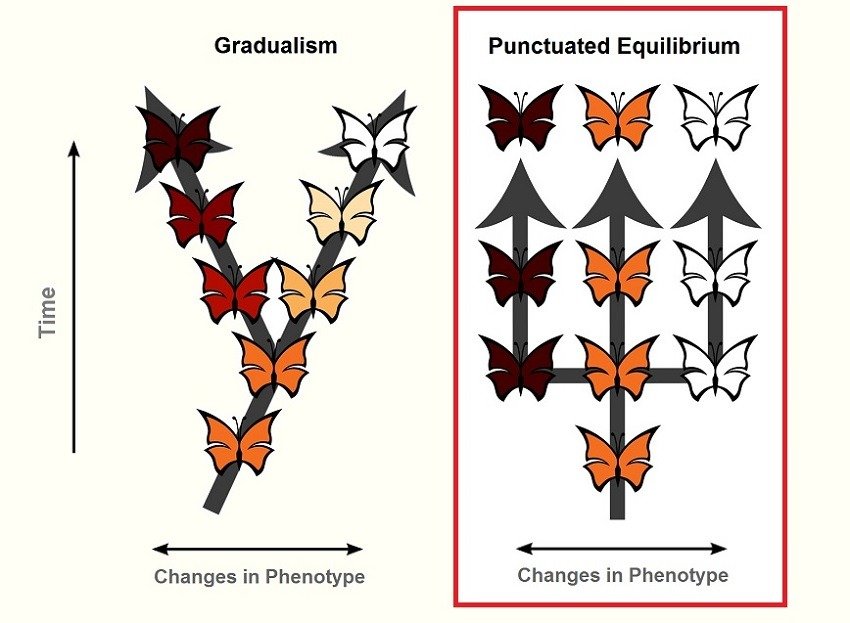
4. The Revelation of Punctuated Equilibrium in Evolutionary Biology
In the realm of evolutionary biology, the concept of punctuated equilibrium represents a significant but often overlooked scientific discovery. Proposed by paleontologists Stephen Jay Gould and Niles Eldredge in the 1970s, punctuated equilibrium challenges the traditional view of gradual, continuous evolution and instead posits that species often undergo long periods of relative stability (stasis) punctuated by sudden and dramatic evolutionary changes. This paradigm-shifting theory has profound implications for our understanding of the patterns and processes of evolution, highlighting the role of rapid speciation events and environmental factors in driving evolutionary transitions. The concept of punctuated equilibrium has sparked extensive debate and furthered our comprehension of the complex dynamics that govern the diversification of life on Earth, offering a nuanced perspective on the tempo and mode of evolutionary change.
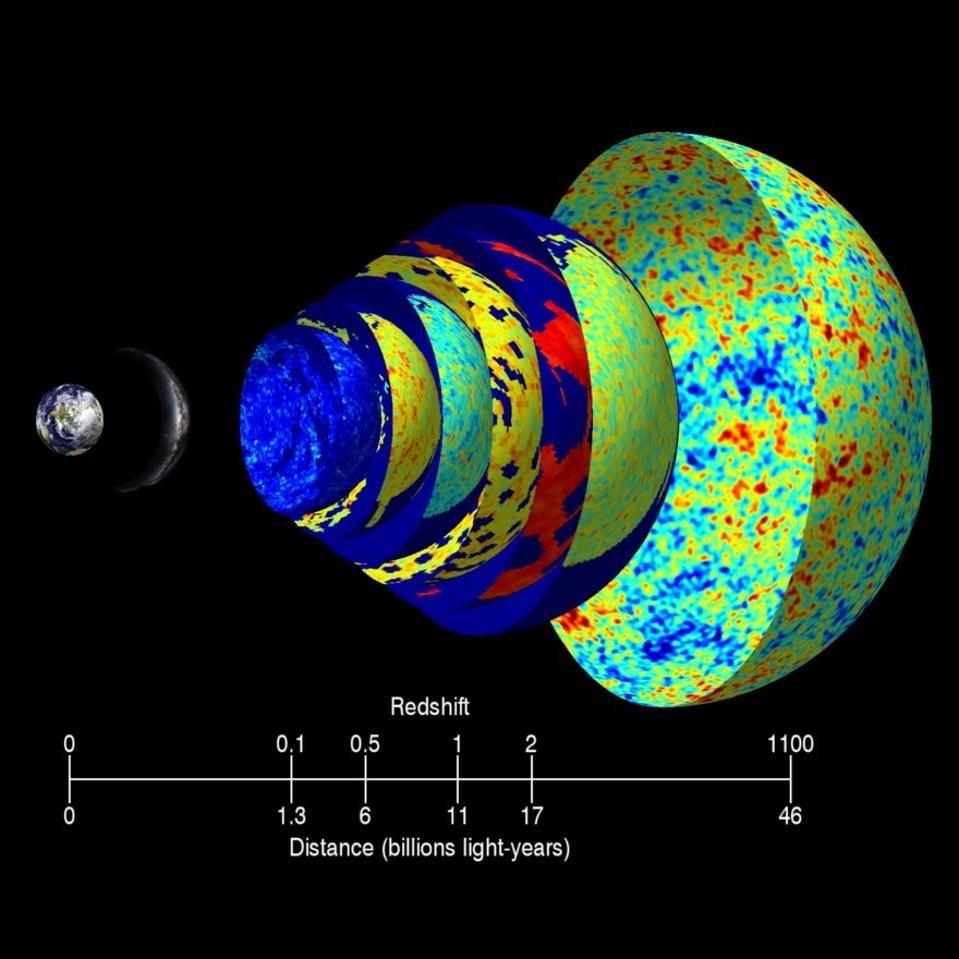
5. The Unveiling of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
One of the most remarkable and relatively lesser-known discoveries in the field of astrophysics is the identification of the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). In 1965, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson serendipitously detected this faint, ubiquitous radiation permeating the universe, providing compelling evidence for the Big Bang theory of the universe’s origin. The discovery of the CMB fundamentally altered our understanding of the cosmos, offering a window into the early stages of the universe and bolstering the prevailing cosmological model. This cosmic relic has since been scrutinized through precise measurements and observations, yielding invaluable insights into the composition, evolution, and large-scale structure of the universe. The revelation of the CMB stands as a testament to the power of serendipity in scientific discovery and has had a transformative impact on our comprehension of the universe’s history and fundamental properties.
These five lesser-known scientific discoveries represent just a handful of the countless breakthroughs that have shaped our understanding of the natural world and propelled scientific progress. While they may not enjoy the same level of recognition as some more widely celebrated discoveries, their significance and enduring impact underscore the immense breadth and depth of human knowledge and ingenuity.